ITIL Service Lifecycle: 5 Stages of the ITIL Service Lifecycle
Introduction
The ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) service lifecycle is a structured framework designed to manage IT services effectively. With the advent of ITIL 4, this framework has been modernized to meet the evolving demands of the digital age. ITIL 4 encompasses all aspects of IT service management (ITSM), guiding organizations in aligning their IT services with business goals. This article explores each stage of the ITIL service lifecycle, highlighting its importance and processes, and illustrating how it contributes to efficient service delivery.
Incorporating ITIL 4 into the management process provides a holistic approach to managing IT services. ITIL 4’s flexible and scalable practices enable organizations to adapt to changes quickly, ensuring that services are delivered efficiently and effectively. By integrating ITIL 4’s principles, organizations can improve their overall service quality, streamline processes, and enhance collaboration between IT and business teams. This results in a more proactive and responsive management process, capable of addressing the dynamic needs of modern businesses.
A crucial component of the ITIL service lifecycle is the service desk, which acts as the primary point of contact between users and IT service providers. The service desk plays a vital role in incident management and request fulfillment, ensuring that users receive timely support and resolutions. By utilizing ITIL 4 guidelines, service desks can improve their efficiency, enhance user satisfaction, and reduce downtime.
Furthermore, ITIL 4’s integration with project management best practices ensures that IT projects are executed smoothly and align with strategic business objectives. Effective project management within the ITIL framework ensures that new services and changes are delivered on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards. This alignment between ITIL 4 and project management fosters better resource utilization, risk management, and continuous improvement, driving successful project outcomes and sustainable IT service management.
What is the ITIL Service Lifecycle?
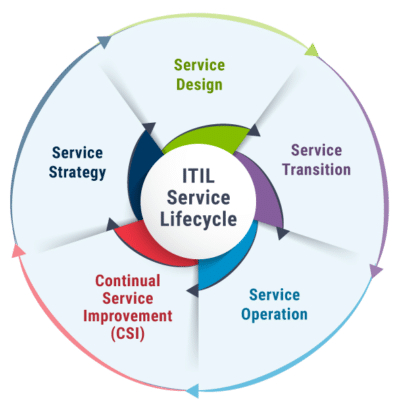
The ITIL service lifecycle, also known as the ITIL lifecycle, comprises five key stages that collectively ensure IT services meet business requirements from initial planning to retirement. Each lifecycle stage encompasses specific processes and activities, enabling comprehensive management of IT services throughout their entire lifecycle.
1. Service Strategy
The Service Strategy stage focuses on setting the strategic direction for IT services. It involves understanding the market, identifying opportunities, and developing plans to meet business needs. Key processes include:
- Strategy Management for IT Services
- Service Portfolio Management
- Demand Management
- Financial Management for IT Services
- Business Relationship Management
Key Processes in Service Strategy
Process |
Description |
|---|---|
| Strategy Management for IT Services | Defines and maintains strategy for IT services. |
| Service Portfolio Management | Manages the service portfolio to align with business goals. |
| Demand Management | Predicts and manages customer demand. |
| Financial Management for IT Services | Oversees budgeting, accounting, and charging for IT services. |
| Business Relationship Management | Maintains positive relationships between the service provider and customers. |
2. Service Design
The Service Design stage translates strategic objectives into detailed service designs. It ensures that new and modified services meet desired business outcomes. Key processes include:
- Service Catalog Management
- Service Level Management
- Capacity Management
- Availability Management
- Service Continuity Management
- Information Security Management
- Supplier Management
Key Processes in Service Design
Process |
Description |
|---|---|
| Service Catalog Management | Maintains a comprehensive catalog of all live IT services. |
| Service Level Management | Establishes and manages service level agreements (SLAs). |
| Capacity Management | Ensures IT infrastructure capacity meets current and future demands. |
| Availability Management | Ensures IT services are consistently available. |
| Service Continuity Management | Prepares for and manages major disruptions to IT services. |
| Information Security Management | Protects the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information. |
| Supplier Management | Manages contracts and relationships with suppliers. |
3. Service Transition
Service Transition focuses on transitioning new or modified services into the live environment efficiently and effectively. It ensures changes are managed in a structured way. Key processes include:
- Transition Planning and Support
- Change Management
- Service Asset and Configuration Management
- Release and Deployment Management
- Service Validation and Testing
- Change Evaluation
- Knowledge Management
Key Processes in Service Transition
Process |
Description |
|---|---|
| Transition Planning and Support | Coordinates resources for a smooth transition of services. |
| Change Management | Controls the lifecycle of all changes. |
| Service Asset and Configuration Management | Manages IT assets and configuration items. |
| Release and Deployment Management | Plans and manages the deployment of releases. |
| Service Validation and Testing | Ensures services meet requirements before deployment. |
| Change Evaluation | Assesses major changes before implementation. |
| Knowledge Management | Facilitates the sharing of knowledge within the organization. |
4. Service Operation
Service Operation ensures that IT services are delivered effectively on a day-to-day basis. It includes processes for managing incidents, problems, and service requests. Key processes include:
- Incident Management
- Problem Management
- Event Management
- Request Fulfillment
- Access Management
Key Processes in Service Operation
Process |
Description |
|---|---|
| Incident Management | Resolves incidents to restore normal service operations quickly. |
| Problem Management | Manages the lifecycle of problems to prevent future incidents. |
| Event Management | Monitors and manages events across the IT infrastructure. |
| Request Fulfillment | Handles service requests from users. |
| Access Management | Controls user access to services. |
5. Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
CSI aims at constantly improving IT services to align them with changing business needs. It involves reviewing performance, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing necessary changes. Key processes include:
- Service Review
- Process Evaluation
- Definition of CSI Initiatives
- Monitoring of CSI Initiatives
Key Processes in Continual Service Improvement
Process |
Description |
|---|---|
| Service Review | Regularly reviews services to find improvement opportunities. |
| Process Evaluation | Assesses the effectiveness of processes. |
| Definition of CSI Initiatives | Identifies and plans improvement initiatives. |
| Monitoring of CSI Initiatives | Tracks the progress of improvement initiatives. |
Benefits of the ITIL Service Lifecycle
Implementing the ITIL service lifecycle provides numerous benefits:
- Improved Service Delivery: Ensures services are aligned with business needs and delivered efficiently throughout the service lifecycle of any product or service offered by an organization.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Improves alignment between IT services and business expectations, leading to higher satisfaction by effectively managing the whole service lifecycle.
- Cost Reduction: Streamlines processes and resource use, resulting in cost savings by leveraging the ITIL service strategy to optimize service performance.
- Better Risk Management: Reduces risks through standardized processes, especially during critical stages of the ITIL lifecycle such as the service transition stage.
- Continual Improvement: Fosters ongoing enhancements to IT services and processes, ensuring better IT service delivery and alignment with evolving business needs.
By implementing the ITIL service lifecycle, organizations can effectively manage IT services from initial concept to day-to-day management. This structured approach not only enhances service delivery and customer satisfaction but also drives continuous improvement, ensuring that IT services consistently meet business goals. The benefits of ITIL extend across the entire lifecycle, providing a robust foundation for achieving long-term success in IT service management.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is ITIL Certification?
ITIL certification validates an individual’s knowledge of ITIL practices and principles. It is valuable for professionals aiming to advance in IT service management.
How do I implement ITIL in my organization?
Implementing ITIL involves understanding the framework, evaluating current ITSM practices, developing a strategic plan, training staff, and gradually adopting ITIL processes. Continuous monitoring and improvement are crucial.
What are the five stages of the ITIL service lifecycle?
The five stages of the ITIL service lifecycle are Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation, and Continual Service Improvement (CSI).
Ready to optimize your IT service management with the ITIL service lifecycle?
Contact Vivantio today!
Schedule a Free Consultation: Discuss your specific needs and explore how implementing the ITIL service lifecycle can elevate your service delivery and align IT with your business goals.
Request a Personalized Demo: Discover how our ITSM solutions can transform your IT operations with:
- Comprehensive Lifecycle Management: Effectively manage the entire service lifecycle from strategy to continual improvement.
- Improved Service Strategy: Align IT services with business objectives for enhanced performance and satisfaction.
- Streamlined Processes: Optimize and automate key ITIL processes to improve efficiency and reduce risks.
- Continuous Improvement: Foster ongoing enhancements to stay ahead in a dynamic business environment.
With our expertise in ITIL, you can achieve both operational excellence and strategic success.